As with the previous line of MET turbochargers, the MET-SE Series is marked by the following characteristics:
- Completely non-water cooled and no sulfuric acid corrosion of the casing
- Inboard beating arrangement for ease of overhaul
- Adoption of plain bearings for long life
In addition, an inner/outer double-walled structure for the gas inlet casing is adopted for ease of release on the turbine side for maintenance checks
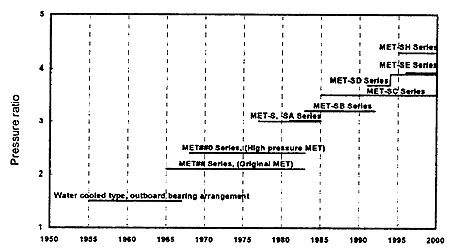
Fig.2 History of MET turbochargers
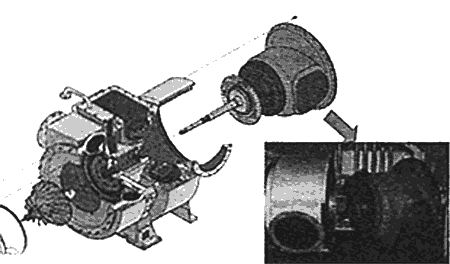
Fig.3 Dismantling of MET-SE turbocharger
MET-SE turbochargers utilize wide chord type blades in the turbine for improved performance in the high pressure ratio region. Fig.4 is a photographic comparison of turbine blades for the MET-SB, -SC, and -SD, and for the MET-SE turbocharger turbines.
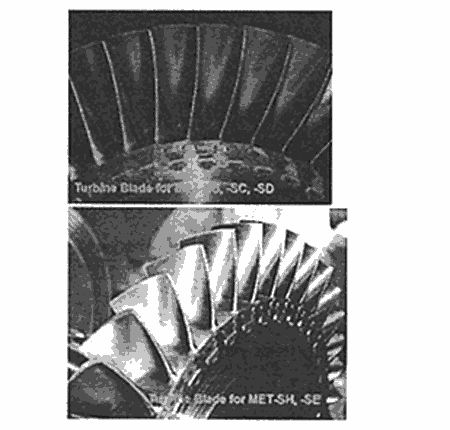
Fig.4 Comparison of turbine blades
3. MET-SE SERIES TURBOCHARGER CAPACITY EXPANSION
3.1 Development objectives
If a turbocharger can be applied for a larger output engine with no change in size, there is obviously no need to increase the size or number of units with increased output of the engine. Also, a reduction can actually be made in the turbocharger model or number of units in cases where engines remain the same. In this sense, there is a need to expand the external form capacity of turbocharger compressors and turbines. Also, as increased engine output is normally accompanied by rising demand for scavenger air pressure, turbocharger compressors for such applications must deliver high pressure ratio performance. In order to increase the capacity of MET-SE turbochargers, the MET-SE II Series was developed using the design modifications presented below.
3.2. High capacity compressor
3.2.1 Aerodynamic performance
The JV3L model impeller wheel was developed to surpass the capacity of the GV3J model, which was formerly the largest capacity compressor impeller wheel in the MET-SE series. Blade height was increased along with the amount of throughput, but without changing the outside diameter of the impeller wheel.
BACK CONTENTS NEXT