|
Annex A
(normative)
Breathing machine outline diagram
A.1 Typical scheme of breathing machine for closed circuits oxygen type
| (拡大画面:17KB) |
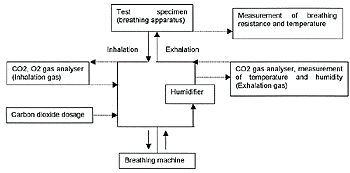 |
The exhalation at performance tests shall be conformed to the following table.
| Minute volume |
CO2 content of exhalation (%) |
Temperature of exhalation |
Humidity(%RH) |
| 20 cycle/min, 1,75 l/stroke |
4,0 |
37 ± 0,5 |
95 to 100 |
| 25 cycle/min, 2,0 l/stroke |
4,5 |
|
Note; The details of machine should be referred to EN400-1992 or recognized national standards.
A.2 Typical scheme of breathing machine for compressed air type
| (拡大画面:17KB) |
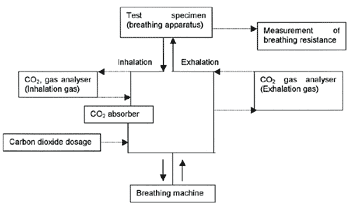
|
The exhalation at performance tests shall be conformed to the following table.
| Minute volume |
CO2 content of exhalation (%) |
Temperature (℃) |
| 20 cycle/min, 1,75 l/stroke |
4,0 |
37,0 ± 0,5 |
| 25 cycle/min, 2,0 l/stroke |
4,5 |
37,0 ± 0,5 |
|
Note; The details of machine should be referred to EN1146-1997 or recognized national standards.
A3 Typical scheme of breathing metabolic simulator for self contained closed-circuit type
| (拡大画面:25KB) |
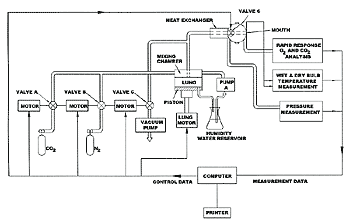 |
| Table A1. Metabolic Parameters - All volumes are adjusted to 37℃, 47 mm Hg water vapour. |
| Minute Volume (VE) |
Oxygen Consumption (VO2) |
Carbon Dioxide Production (VCO2) |
| 35 l/min (20 x 1.75 l/m) |
1.58 l/min |
1.58 l/min |
| 50 l/min (25 x 2,0 l/min) |
[3.50] l/min |
[3.50] l/min |
|
Operation: Gas ventilation is achieved through a stepper motor controlled piston programmed to produce the desired sinusoidal waveform. Breathing resistance, wet and dry bulb temperature, and oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration are continuously measured at the mouth during both inhalation and exhalation. Oxygen removal is achieved by continually withdrawing gas from the system through stepper motor controlled needle valve C; the removal rate determined by the average oxygen concentration measured at the mouth. Carbon dioxide production is simulated by injecting carbon dioxide into the system through stepper motor controlled needle valve A at a rate equal to the desired VCO2 plus the amount of CO2 exhausted through valve C. Nitrogen is introduced into the system through stepper motor controlled valve B to replace nitrogen gas exhausted through valve C. Water vapour is derived continuously from fast response wet and dry bulb temperature measurements, calculated within the system software. The lung is heated and humidified to condition the exhaled gas to 37 ℃, 95 to 100% relative humidity.
(normative)
Practical performance test procedure
B.1 Standard procedure of practical performance test
| (拡大画面:37KB) |
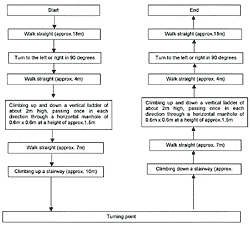 |
(Informative)
Bibliography
EN 400: 1993, Respiratory protective devices for self-rescue − Self-contained closed circuit breathing apparatus − Compressed oxygen escape apparatus − Requirements, testing, marking
EN 1146: 1997 Respiratory protective devices for self-rescue − Self-contained open-circuit compressed air breathing apparatus incorporating a hood (compressed air escape apparatus with hood) − Requirements, testing, marking
EN 12021: 1998, Respiratory protective devices - Compressed air for breathing apparatus
|