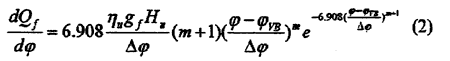TS-125
A Simulation Study on Diesel Engine Performance Failure
Yihuai Hu * Biyll Wan **
ABSTRACT
A computer program has been developed in order to simulate the operational behavior of a diesel engine under different performance failures and running conditions.
The simulation models of a four-stroke, turbocharged diesel engine and the simulation results by the use of these models are briefly described. The calculation results, which are obtained in terms of relative deviation form the normal performance, show the relations along thermodynamic variables, performance failures, running conditions and ship operation conditions. The simulation results also that there is a strong simulating in the relative exhibition of thermodynamic variables under different running conditions. This similarity could be utilized as a new information source for failure detection. Correlative analyses are also made on the simulated results to determine the optional selection of symptomatic parameters in order to reduce the modeling scale.
Finally an example is introduced in order to verify the feasibility of relative deviation analysis by the use of an artificial neural network method for diesel engine failure diagnosis.
Key Words: Diesel Engine, Failure Simulation, Deviation Analysis, Multivariate Analysis, Artificial Neural Network
1. INTRODUCTION
Condition monitoring and failure diagnosis techniques are considered of major importance for higher reliability and can be of great benefits on reducing manning cost, especially for big and critical systems machinery such as gas-turbines, aircraft, nuclear power stations and marine engines. With several unique properties of little disturbance from outside, high quality of information wide range for diagnosis and strong availability in application the thermodynamic variables of diesel engine are usually regarded as the most abundant symptomatic source for failure diagnosis. Large bore marine diesel engine is a complex system composted of mechanical, electronic, thermal and hydraulic subsystems. This kind of system al ways has lots of failure motivating sources and confusing symptoms. Simple corresponding regularity among them does not exist. Influences of some a failure to symptomatic parameters and sensitivities of some a parameter to performance failures are usually changeable with engine running condition and ship operation condition. Most of knowledge about relations between performance failures and thermodynamic variables is mainly from experiments and experience, which is vague and limited to a great extent due to shortage of systematic analysis and quantitative description. Experimental modeling of big, complex diesel engine for failure diagnosis is very difficult and dangerous. This situation has been the "bottleneck" in intelligent failure diagnosis of marine diesel engine.
Filling and emptying diesel engine simulation model has been successfully used in design for many years and is being used in ship management system for advanced control and performance optimization. By careful selection of model coefficients this simulation program can be also used to simulate some performance failures. The calculated results will give us a more complete understanding of failures' behaviors under different running conditions, can help us to detect the failures amongst complex symptoms and, if accurate enough, provide modeling specimen for artificial neural network in failure diagnosis of marine diesel engine. Compared to experiments on board ship this simulative modeling method possesses advantages of shorter studying period, less research investment, lower risk in failure simulation and more symptomatic information.
2. SIMULATION MODEL
The engine model referred to in this paper is a general-purpose engine thermodynamic simulation code [1]. This model is the control volume type, which treats a multi-cylinder engine as a series of thermodynamic control volumes interconnected through valves and ports. Several modifications have been made to meet the demand for failure simulation and performance prediction at full running conditions briefly described below:
To take into account the influence of performance failures to combustion procedure, a term, which is called combustion efficiency, was inducted into the Vibe's function. The term is defined as the ratio of completely-burned fuel and injected fuel which is the function of excess air factor α defined as [2].
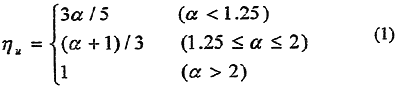
Then the rate of heat release can be defined as