3. STATISTICAL ENERGY ANALYSIS
SEA is a strong tool to predict noise and vibration of complex and large structure especially in high frequency range. In SEA, the structure is divided into some subsystems. The SEA basic equation is given as a power flow relation among subsystems. This equation is simple, but it is generally difficult to estimate the parameters included the equation.
Consider the case that the structure can be divided into two subsystems shown in Figure 1. The power flow equation is
P1 = ωη1E1a) + ωn1η12(E1/n1 - E2/n2)
P2 = ωη2E2a) + ωn2η21(E2/n2 - E1/n1) (1)
where ω is center frequency of a frequency band. Pi, Ei, ni are power input, noise/vibration energy and modal density of subsystem i, respectively. ηi is internal loss factor of subsystem i and ηij is coupling loss factor from subsystem i to j.
The ILF expresses the attenuation in subsystem. The factor is difficult to estimate theoretically and then it is determined by experiment. The CLF and the modal density for flexural wave are theoretically evaluated by equations (2) and (3) if the subsystem is plate.
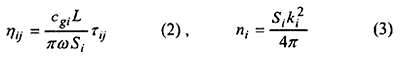
Where cgi, Si, ki are flexural group wave velocity, surface area and wave number of subsystem I, respectively. And L is the coupling length between subsystem I and j, and τij is transmission efficiency from subsystem I to j.
Thus, the determination of ILF and CLF brings the energy levels of subsystems under arbitrary conditions by simple matrix calculation shown in equation (1).
4. NOISE ESTIMATION PROGRAM OF SHIP KNOISE
4.1 Outline
KNOISE has been derived from CABlNOISE [6] which was developed by NKK CORPORATION and NK about 15 years ago. While CABlNOISE was originally developed for a mainframe computer, KNOISE has been ported to a personal computer and improved by adding the graphical user interface, etc. One of main goals of KNOISE is to estimate noise levels of the accommodation space and the machinery space at the design stage. The methodology for the prediction used in KNOISE is based on SEA mentioned before. Various parameters necessary for the calculation in KNOISE is determined from the experimental values which have been obtained by the field measurement of the real ship or the noise source such as the diesel engine. For the new type of ship such that the acoustical properties is unknown, there is a function that the parameters can be calculated from the comparison between the calculated results and the measurement results.
The model for the calculation in NOISE, which represents the structure of the accommodation space and the machinery space, consists of several thousands of elements corresponding to the room, the floor, the wall, the ceiling, etc. The noise level of the cabin in the accommodation space or in the engine room or the flow of the noise energy among the elements can be estimated by KNOISE. In the SEA method, the propagation of the noise energy among the elements in the model must be considered. But, in case of the large-sized construct such as the ship, the cost to prepare the model becomes high because the amount of the data for the model is large. Therefore, the special consideration has been given, that is, the hull structures in front of the engine room and to the rear of the engine room are omitted by replacing the energy transmitted from the engine room to these parts by increasing the loss factor of the bulkhead at the boundary.
KNOISE can be applicable to the large general merchant ship which has the fold part and the engine room under the accommodation space like the tanker and the cargo vessel. The calculation is carried out with the individual octave band which has the center frequency from 31.5Hz to the 8000HZ respectively. The program can be operated under the Windows95/98/2000.
KNOISE consists of following three modules: KNOISE Preprocessor, KNOISE Solver, and KNOISE Postprocessor. The individual modules are described below. (see Figure 2)
4.2 Function
4.2.1 KNOISE Preprocessor
In the step to make the data, the data to describe the geometric structure of the basic cabin arrangement and the machinery space can be inputted by using the gui. General specifications for the cabin and the machinery, space are prepared in the database (hereafter, refereed to "standard spec. table"). In addition, the detailed data of each element can be changed by indicating the position to be changed and the one to be inputted. There are following three kinds of data in the modeling.
・Element
a) General data
The general data is the input data which is common to all layers (Corresponding to deck in general).
b) Layer data
The layer data represents the layout of the accommodation or machinery space.