3. 2 The generating method of abnormal conditions of gas pressures in cylinder.
For the method of generating abnormal conditions of gas pressure in cylinder artificially, the test was carried out with the nozzles of fuel injection valve decreased numbers of holes but not changed the diameter of holes. It was on the assumption of the clogged nozzle hole.
3. 3 Analysis and examinations of the operation management method.
3. 3. 1 Calculation of the effective length of the crankshaft.
The effective length of crankshaft is needed to be evaluated that the crank arms are the solid round shaft of the equal sectional area having the equivalent torsional stiffness, what is called, it must be converted into the equivalent shaft length. Although some kinds of calculation formulas are proposed as the converting method to the equivalent length, the equivalent length will become more or less different depending on the calculation formula to be applied, In this case, the equivalent length is calculated backward being based on the torsion angle of the crankshaft when the engine is operated in normal condition.
3. 3. 2 Separation of the torque by the inertia force of the reciprocating mass.
In case of observation of the abnormal condition of the gas pressure in cylinders, the diagnostic accuracy can be improve by extracting only the gas pressure components.
The torsion angles by the inertia force of the reciprocating mass were calculated by the Eq. (4) and (5). And these were shown in Fig. 7.
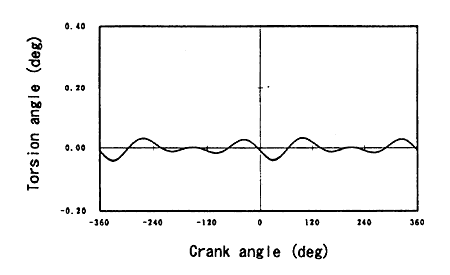
Fig. 7 Torsion angles by the inertia force
3. 3. 3 Comparison between the measured data and calculated results.
Fig. 8 shows the comparison between the measured torsion angle form and that of obtained by the calculation.
Although the torsional vibration components are included in the actually measured form, it can be said that the basic patterns of both forms coincide very well.
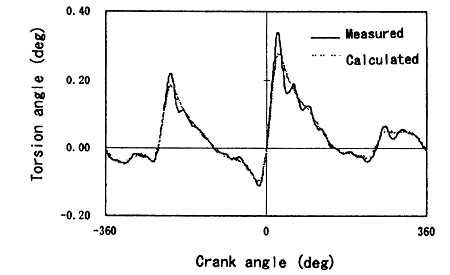
Fig. 8 Comparison of torsion angles between the measured data and the calculated results
3. 3. 4 Considerations for Torsional vibration of the shafting.
In the torsion angles of the crankshaft during the engine operation, naturally the components being caused by the torsional vibration of the whole shafting are included.
Fig. 9 shows the difference between the measured torsion angle form and that of obtained by the calculation. This form is exactly the response of torsional vibration of the crankshaft.
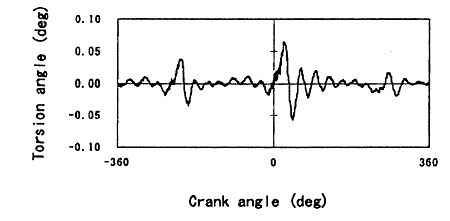
Fig. 9 Difference between measured form and calculated one
For the purpose of separation this torsional vibration components from the measured crankshaft torsion angles, it is necessary to make clear the relations of the compelling force, attenuation and the phase, and to work out exactly the response of torsional vibration. Unfortunately, the accurate simulations of these torsional vibration responses including the phase relations are difficult. However, for the purpose of watching the abnormal conditions of gas pressures in cylinder,including the torsional vibration responses, we concluded that the sufficient diagnostic accuracy could be obtained in overall evaluation. Thus in this case, the separation of these torsional vibration components was not carried out.
BACK CONTENTS NEXT