This low pressure saturated steam and liquid were applied to the rivet layer packed in the container, and the de-oiling effect and the characteristics of steam was studied. In this study, test machine parts is two kinds of small rivets and the waste such as Fig.2. The height of rivets bet in the test section was 110 mm, and bottom of bet was supported by a net. The test time was 1 minute, the hot water flow rate was 0.22〜0.24 l/rain, the hot water temperature was 50〜80℃ and the vacuum was 500〜700 mmHg.
3. Results
3.1 De-oiling experiment
The experimental results are classified into 4 types by the visual observation for residual oil. The de-oiled rivets were spread to a white paper, and left over 12 hours, and removed from the paper. The effect of de-oiling was evaluated according to the area of the remained oil spots on the paper. The best result was named as "very good" remaining no spots. The next one was named as "good" remaining a few spots area, and the next one was named as "a little oily" remaining several spots. And the worst one was named as "very oily" remaining a wide spread of oil. The area of the oil spots before de-oiling rivets and "very oily" case were almost the same. Shown in Fig.3 is a photograph of "very oily" rivets.
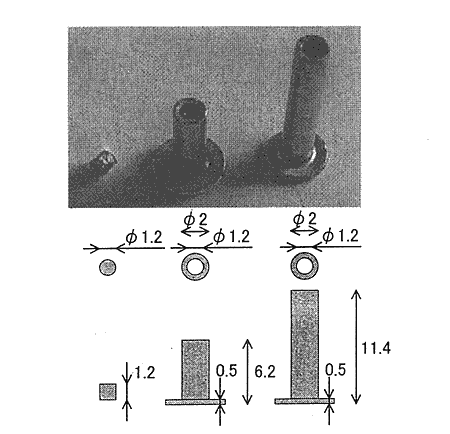
Fig.2 Schematic of sample rivets
Fig.3 "very oily" rivets
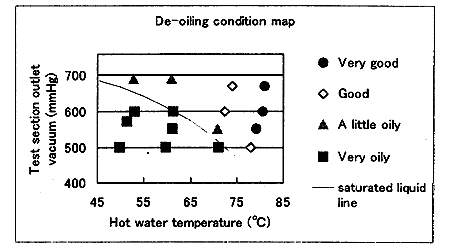
Fig.4 De-oiling condition map at hot water rate 0.22 - 0.24 l/min
Shown in Fig.4 is the map of the de-oiling condition in the relation of the test section outlet vacuum and hot water temperature. The "very good" results exist in the region of the high water temperature and high vacuum. The flow pattern in the test section at this region was annular flow. The "very oily" results exist in the region of the low hot water temperature and test section outlet vacuum. In the test section at this region no flashing was observed. A small amount of saturated steam generated by the flashing in the rivet layer can easily enter into the cavity of rivets. It is considered that the steam molecule collide and scrub the oil from the rivets. The liquid water can't enter into the cavity of rivets that diameter is 1.2 mm. The surface tension of liquid water prevents the water from entering into the small cavity. It is considered that the mechanism of the de-oiling is due to scrubbing the oil from machine parts by the impact of collision with the molecules of water.
3.2 Characteristic of steam flow experiment
Shown in Fig.5 is the relation between the pressure difference of the rivet layer divided by the rivet layer inlet pressure and temperature of the rivet layer inlet for the rivets of 6.2 mm in length. One-dimensional analysis assuming the isoenthalpic change was conducted. The rivet bet was divided into 20 nodings in the flow direction. The difference of pressure[2-4] at the very small height dH is:
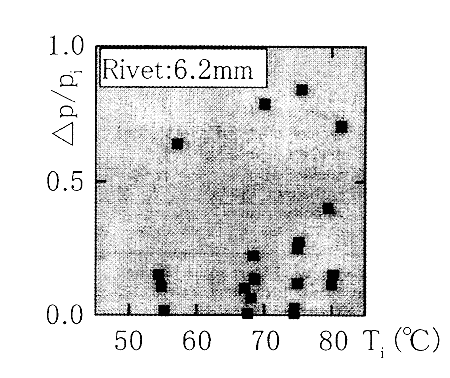
Fig.5 Pressure difference of rivet layer
BACK CONTENTS NEXT