Also, from (2), the exhaust-gas temperature equation is written as:
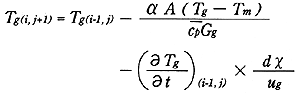
2] Engine Combustion Cycle Component Model
The plant dynamic characteristics, or response time, at issue is far longer than the engine combustion cycle response time, so the change in engine combustion cycle by itself exerts no serious effect on the entire plant dynamic characteristics. To reduce the computation load, therefore, the combustion in the engine cylinders was represented by a simplified model in the same manner as the SCR system.
In other words, the rate of combustion gas flow through the engine equivalent area at the scavenging-exhaust pressure ratio was calculated by the adiabatic flow equation, and for the output required of the generator the necessary fuel injection quantity as well as the rate of heat loss and mechanical loss were imparted to the engine output, and then using excess air ratio λ calculated from the fuel quantity and applicable air weight the combustion efficiency ηcomb was calculated to determine the quantity of heat produced in the cylinder.
ηcomb = 1- exp (-aλ) α= 15
Also, from the enthalpy balance expressed as follows, the exhaust-gas temperature Te was calculated.
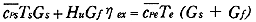
3] Gas-Extraction Valve Computation Model
A gas-extraction valve was installed before the turbocharger gas inlet for valve open area data input with time. It was so arranged that the exhaust gases released through the gas-extraction valve would be led into the exhaust-gas duct after the turbocharger.
Evaluation of Numerical Plant Dynamics Simulator for Propriety
The numerical plant dynamics simulator was evaluated for its propriety through comparative studies of measured and calculated results.
Fig. 6 shows for comparison the turbocharger speeds and engine exhaust-gas temperature as determined by measurement and calculation when the engine output was reduced from 2800 kW to 2400 kW. The calculated values, determined employing the SCR system heat capacity, heat loss, rate of heat exchange between exhaust gases and SCR system, and other data related to heat exchange occurring in the SCR system after adjusting them to proper levels, show that with the only exception of the calculated turbocharger speed variations exhibiting a small disagreement with the measured values, the calculated results as regards both the period and amplitude of the fluctuations in the engine exhaust-gas temperature. It therefore was decided that the simulator programs could closely simulate the real-life situations.
Fig. 6 Comparison of Calculation Result and Measurement Result
Confirmation of Effectiveness of Gas-Extraction Valve in Restraining Hunting
The effectiveness of the use of the gas-extraction valve in restraining the hunting in scavenging and exhaust circuits was confirmed using the numerical plant dynamics simulator devised this time.
Fig. 7 shows the results obtained by calculation assuming the gas-extraction valve to perform open/close operations in the process of the engine output going down from 2800 kW to 2400 kW. As indicated in Fig. 7, though the gas-extraction valve was set to open and close on the three different conditions, in every instance the valve is shown to have opened simultaneously with the decline in engine output and to have closed again following the end of decline in engine output.
It is observed from Fig. 7 that the effectiveness of the gas-extraction valve in restraining the hunting somewhat varies with the conditions employed for its open/close operations, falling at times to completely restrain the hunting. As against the case of the gas-extraction valve remaining inactive allowing the engine exhaust-gas temperature to fluctuate in hunting to the point of divergence, however, the dark solid line representing the calculated results, for example, shows that the gas-extraction valve opens 3 cm2 in 400 sec. At the same time that the engine output goes down and, after remaining in the same open position for 100 sec. Following the end of decline in engine output, closes in 800 sec. leaving the exhaust-gas temperature free of hunting and in the very stabilized state.