Only the data for 50% load was collected with MDF (A). The exhaust gas concentration was compared after it was converted into the value under 13% O2 concentration.
3.2.1 NOx
Fig. 13 shows the change in the NOx concentration to the presence/absence of the pouring of the reducing agent. It is understood that the NOx concentration is greatly reduced by pouring the reducing agent.
3.2.2 N2O
Fig. 14 shows the change in the N2O concentration to the presence/absence of the pouring of the reducing agent. It is also understood that N2O as well as NOx is reduced in concentration by pouring the reducing agent. Fig. 15 shows the example of measurement, and it is understood that N2O as well as NOx is greatly reduced by pouring the reducing agent.
It is well known that N2O is reacted in the extinguishing reaction in addition to the generating reaction with NOx5).
H + N2O → N2 + OH
O + N2O → N2 + O2
→ NO + NO
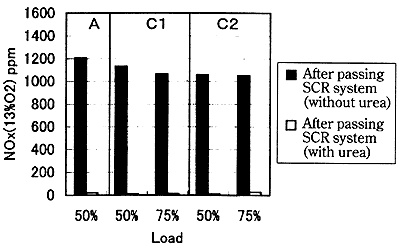
Fig. 13 Effect of SCR system on NOx
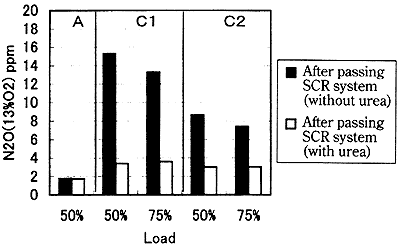
Fig. 14 Effect of SCR system on N2O
It is believed that the N2O concentration is reduced as shown in Fig. 15 as the result that the decomposing reaction of N2O by the hydrogen radical (H) and the oxygen radical (O) to be generated in the process of the NOx-removal reaction exceeds the generating reaction of N2O by NOx. Though there is a report5) that N2O is generated by the use of the SCR system (with the catalyst of precious metal), it is understood that not only NOx but also N2O can be reduced by this tested catalyst.
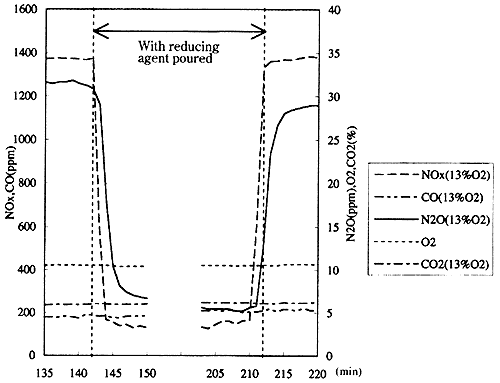
Fig. 15 Example of measurement of exhaust gas at outlet of SCR system (75% engine load, with fuel C1)
3.2.3 HC
Fig. 16 shows the HC concentration to the presence/absence of the pouring of the reducing agent. It is shown from this figure that HC is also reduced by pouring the reducing agent. This is believed attributable to the fact that the deNOx reaction which is the exothermic reaction is generated by pouring the reducing agent, the temperature of the exhaust gas rises, and the oxidizing reaction of HC is promoted thereby. The temperature of the exhaust gas in the SCR system which was approximately 350℃ and 400℃ in 50% load and 75% load rose by approximately 25℃ by pouring the reducing agent. It is considered that HC is reduced in the reaction with oxygen in the exhaust gas, and due to the function of HC as the reducing agent of NOx.
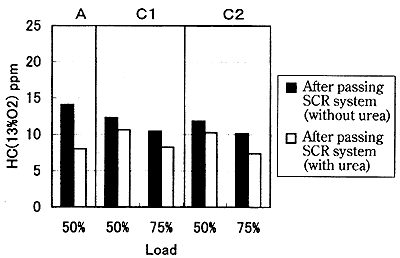
Fig. 16 Effect of SCR system on HC
BACK CONTENTS NEXT