e is the void ratio defined by the following formula:
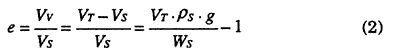
where,
VV and are volumes of void space and solid in the total volume VT, respectively;
ρS is solid density;
g is gravity acceleration; and
WS is dry weight corresponding to VS.
The resisting tangential coefficient tanψ, i.e., the internal friction coefficient obtained through direct shear tests, is the inclination of the graph. The cohesion c is the resisting tangential stress where normal stress equals to zero. It should be noted that the shear strength of wet nickel ore obtained through direct shear tests and one obtained through triaxial compression tests showed good agreement 3), 5).
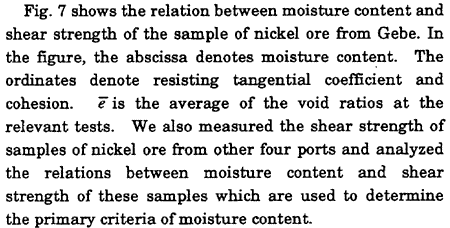
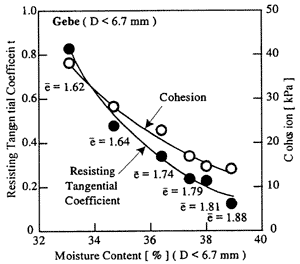
Fig. 7. Relation between moisture content and shear strength
We carried out two-dimensional numerical calculation of sliding failure in the same way as that for the slope stability calculations utilized in soil mechanics based on the relation between moisture content and shear strength and on the average density of the samples for direct shear tests. 3), 6) As illustrated in Fig. 8, the safety factor corresponding to sliding line, which is assumed to be an arc, is calculated by "Fellenius method", and the danger of sliding failure is indicated by "critical safety factor", i.e., the minimum value of safety factors obtained through calculations changing sliding lines.
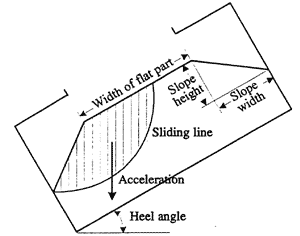
Fig. 8. Slope stability calculation
In order to maintain the slope stability for important structure under construction, the critical safety factor derived by this calculation method should generally be kept at least 1.2. To prevent sliding failure of solid bulk cargoes, it can analogically be said that the critical safety factor should be kept not less than 1.2 during transportation.
Table 6. Conditions of slope stability cal.
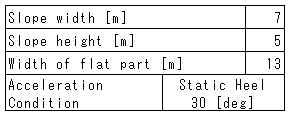
Table 6 shows the conditions of calculation determined based on the investigation of the shapes of cargo piles. Fig. 9 shows the relation between moisture content and critical safety factor of the sample from Gebe.
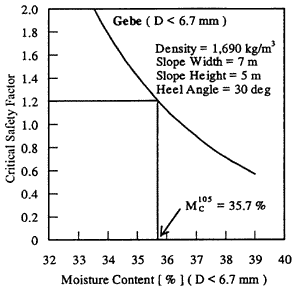
Fig. 9. Relation between moisture content and slope stability
In the figure, the abscissa and ordinate denote moisture content and critical safety factor, respectively. The moisture content corresponding to the critical safety factor 1.2, i.e., the primary criterion of moisture content for preventing sliding failure, is 35.7 %. Similarly, the primary criteria of moisture content of the other samples were analyzed and the results are shown in Table 7.
前ページ 目次へ 次ページ