2.3. Insertion of the sample into the mould
Taking the maximum grain size of the sample and clearance between the cone (c.f. 2.4) and the mould into consideration, we specified the diameter and the capacity of the mould at 150 mm and 4,000 cm3, respectively, as illustrated in Fig. 3.
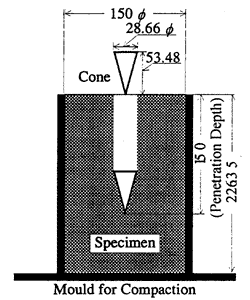
Fig. 3. Specification of the cone and the mould
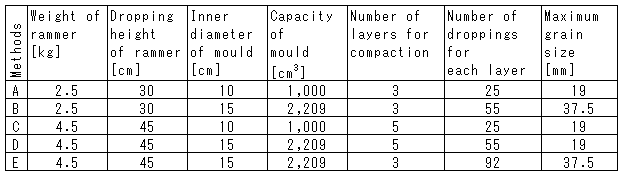
We specified the compaction procedure based on the standard, JIS A 1210: 1999, i.e., "Test method for soil compaction using a rammer". Table 3 shows five methods for compaction described in the standard. The inner diameter of the mould and maximum grain size of the sample for method "D" in the table are the same those for the new test procedure. Considering the deal of work
Table 3. Conditions for compaction in JIS A 1210
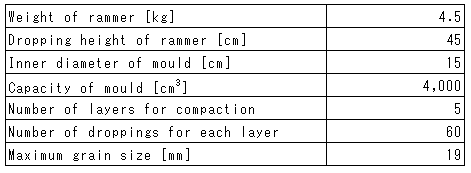
for compaction and capacity of the mould, we specified the conditions of compaction as shown in Table 4 based on the method "D" described in Table 3. The compactive effort, i.e., the energy of compaction per unit volume, of the new test procedure is approximately 60 % of the one for the method "D" described in Table 3.
Table 4. Condition of compaction in the new test procedure
After the compaction of the sample, the surface of the specimen is formed by leveling off the sample along the brim of the mould.
2.4. Cone penetration test
The cone penetrometer, i.e., the equipment for measuring the cone penetrating force shown in Fig. 4, with the cone of larger type of which the base area is 6.45 cm2 is selected for the new test procedure. The speed of penetration is specified at 1 cm/sec, according to standards and the depth of penetration is specified at 15 cm. The maximum value of cone penetrating force is measured during the penetration of cone into specimen until the top the cone reaches to 15 cm from the brim of the mould.
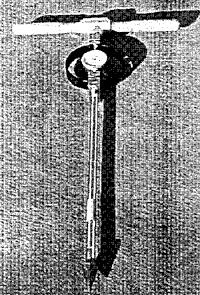
Fig. 4. Cone penetrometer
2.5. Number of repetition of cone penetration tests and the representing value
Cone penetrating force sometimes reaches high resulted from confinement of penetration due to comparatively large particles, even the specimen is formed with particles less than 19 mm. Such phenomenon affects the maximum cone penetrating forces obtained through the cone penetration tests. The results of the tests should be represented by the minimum value of the maximum cone penetrating forces obtained through the tests in order to reduce the effect of such phenomenon on the repeatability of representing value of the results.
Forming specimen for each test using the same sample, we repeated the cone penetration tests 30 times to investigate the effect of number of repetition of the tests on the repeatability of representing cone penetrating force.
前ページ 目次へ 次ページ