| (拡大画面:196KB) |
 |
| (拡大画面:85KB) |
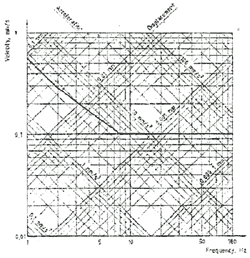 |
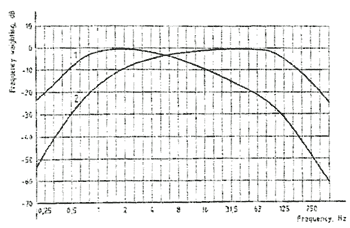
Figure B.1 - Human sensitivity curve
| (拡大画面:41KB) |
 |
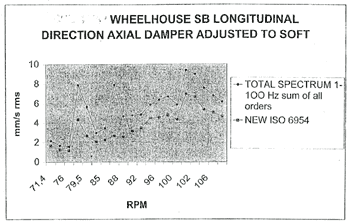
WHEELHOUSE SB LONGITUDINAL DIRECTION AXIAL DAMPER ADJUSTED TO SOFT
| (拡大画面:52KB) |
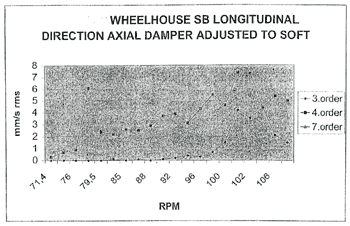 |
WHEELHOUSE SB LONGITUDINAL DIRECTION AXIAL DAMPER ADJUSTED TO SOFT
| (拡大画面:46KB) |
 |
ISO 6954:2000(E)
7 Evaluation of habitability
It is recommended that the classification to be applied to the various areas of a ship be agreed between the interested parties (e.g. shipbuilder and shipowner) prior to any assessment of the habitability.
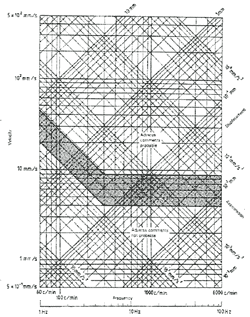
Table 1 contains guidelines for the values above which adverse comments are probable, and values below which adverse comments are not probable. The values are expressed in terms of the overall frequency-weighted r.m.s. acceleration (mm/s2) and overall frequency-weighted r.m.s. velocity (mm/s) in the range 1 Hz to 80 Hz. The human sensitivity curve on which the frequency-weighting curves are based is shown for deeper understanding in annex B.
Table 1 - |
Overall frequency-weighted r.m.s. values from 1 Hz to 50 Hz given as guidelines for the habitability of different areas on a ship |
| Area classification |
| |
A |
B |
C |
| Values above which adverse comments are probable |
145 |
4 |
214 |
6 |
286 |
8 |
| Values below which adverse comments are not probable |
71.5 |
2 |
107 |
3 |
143 |
4 |
| NOTE The zone between upper and lower values reflects the shipboard vioration environment commonly experienced and accepted. |
|
Three different classification areas are presented.
- Classification A:
- Classification B:
- Classification C:
NOTE For guidance, Classification A can be passenger cabins. Classification B crew accommodation areas, and Classification C working area.
8 Test report
The testreport shall, as a minimum, contain the following information and data;
a) reference to this international Standard;
b) place and date of the test, identification of persons and organizations performing the test;
c) principal ship design characteristics;
d) actual conditions of ship and environment experienced during the test;
e) locations and orientations of the transducers;
f) recording equipment and calibration procedure;
g) results of the measurements.
An example of a report is shown in annex C.
© ISO 2000 - All rights reserve
|