
Table. 4 Experimental Engine Specifications
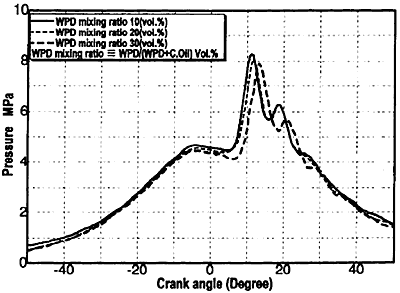
Fig.6 Pressure Diagram
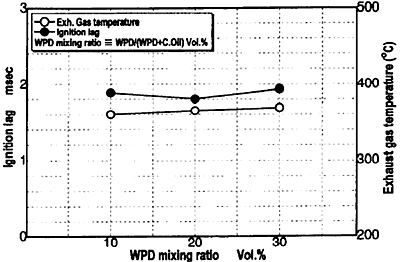
Fig.7 Change in Lag and Exhaust Gas Temperature
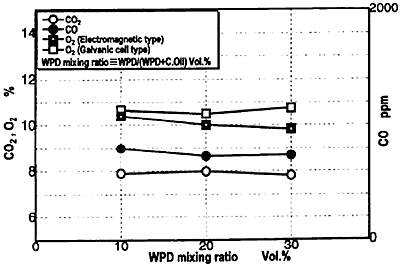
Fig.8 Change in CO2, CO, O2 Concetration
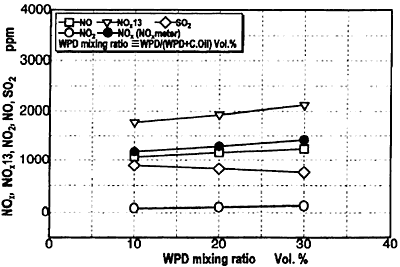
Fig.9 Change in NOx, NOx13, NO2, NO, SO2 Concentration
Table 4 states the experimental conditions, in which the engine speed and load are kept constant at 2200 rpm and 75% of continuous rated output while the mixing ratio has been changed from 10 to 20 and 30 vol.%. The experiments were carried out without preheating the fuel oil, under atmospheric temperature (about 25℃).
4. Results and Discussions
Figure 6 shows the combustion pressure diagram. Along with the increase of WPD mixing ratio, although exhaust gas temperature does not change the maximum combustion pressure decreases and the combustion retards. Figure 7 indicates the change in ignition lag and exhaust gas temperature. Figures 8 and 9 show the change in the concentration of components of the exhaust gas. Regardless of the change in the WPD ratio CO, CO2, O2 concentration is stable around 700 ppm, 8%, and 10.5% respectively. However, as the WPD mixing ratio increases NOx concentration gradually increase 19% from 1180 to 1400 ppm due to the rise in combustion temperature.
BACK CONTENTS NEXT