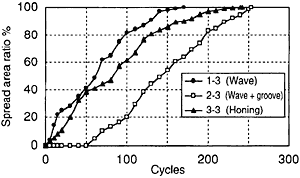
Fig.5 Spreadability of cylinder oil (0.01 cc/ome feed, 70 rpm)
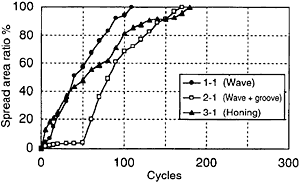
Fig.6 Spreadability of cylinder oil (0.02 cc/ome feed, 70 rpm)
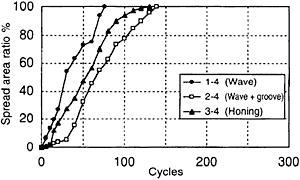
Fig.7 Spreadability of cylinder oil (0.03 cc/ome feed, 70 rpm)
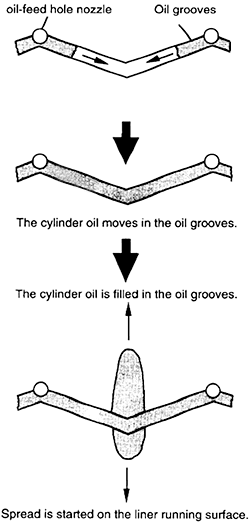
Fig.8 Spreading condition of cylinder oil in oil groove
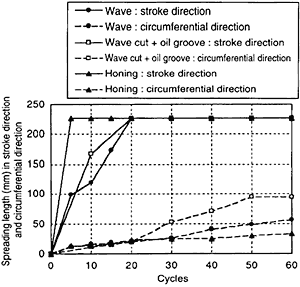
Fig.9 Spreadability of stroke direction and circumferential direction (0.02/ome feed, 70 rpm)
In order to further examine the characteristics of the spreading condition, Fig.9 shows the results of the spread length in the stroke direction and the circumferential direction is examined for the oil feed quantity of 0.02 cc/ome feed. With the wave cut together with the oil groove, there is a time delay before the cylinder oil is filled in the oil groove as described above. However, in the running condition of the actual engine, the cylinder oil is continuously fed, and the oil groove are considered to be constantly filled, and thus, the cycle at which the cylinder oil is started to spread on the liner surface is moved to the zero point in Fig.9.
The spreadability in the stroke direction is more excellent with the honing, while the spreadability in the circumferential direction is excellent in the order of (wave cut together with oil groove) > (wave cut) > (honing).
BACK CONTENTS NEXT