This is due to its less heat exchange efficiency and bigger air flow resistance.
Deposited turbine nozzle (1) increases gas exhaust manifold pressure Pbt and turbocharger running speed Ntc. This therefore makes the rise in compressor discharge air temperature Tk and pressure Pk, maximum gas combustion tempera P=max and temperature difference of inter-cooler DTk due to the increase of circling airflow Gk. Worn turbocharger bearing (m) affects turbocharger's working efficiency and has just a opposite symptom due to the decrease of circling air flow Gk
Retarded injection timing (o) and worn fuel pump plunger (p) have very similar symptoms of the most obvious rise in temperature difference of inter-cooler and obvious increase in compressor discharge air temperature Tk, maximum gas combustion pressure P=max, gas exhaust manifold temperature Tbt and pressure Pbt, turbocharger running speed Ntc and fuel consumption ratio Ge. This is mainly because the too late injection timing increases the diffusion combustion and worn pump plunger harms the fuel atomization which all worsen the combustion inside combustion chamber. Diesel engine needed more fuel and more fresh air to supply the same power under the same running speed.
Rotated ship rudder angle (q) and encountered strong wind (r) during navigation enlarge ship's resistance and need bigger engine power for the same running speed This brings with the increase in most of variables similar to retarded injection timing and worn fuel pump plunger failures. Ambient temperature (b) & (c) has some influence on engine performance. With lower ambient temperature the temperature difference of inter-cooler DTk descends greatly and compressor discharge air temperature Tk drops obviously. So in practical failure diagnosis ship navigation condition and weather condition that have to be taken into account.
Due to the inherent relations beyond diesel engine working principle some variables always have congruent behavior such as compressor discharge air pressure Pk and air intake manifold pressure Ps. It is necessary to make some cancellations of variables to simplify the modeling process in practical failure diagnosis. Comparing Fig.1 and Fig. 2 it is found that relative deviations represent very similar tends in different performance failures at rated condition and partial condition. It is implied that relative deviations can be utilized as symptomatic parameters even diesel engine thermodynamic variables usually vary within very wide range at different running conditions. In this way engine conditions can be taken into account and artificial neural network method can be used in diesel engine failure diagnosis without to much modeling work and greater difficulty.
4. CORRELATIVE ANALYSIS
Relative deviation of all simulated variables including compressor air flow Gk and cycle fuel consumption gf are expressed as matrix A
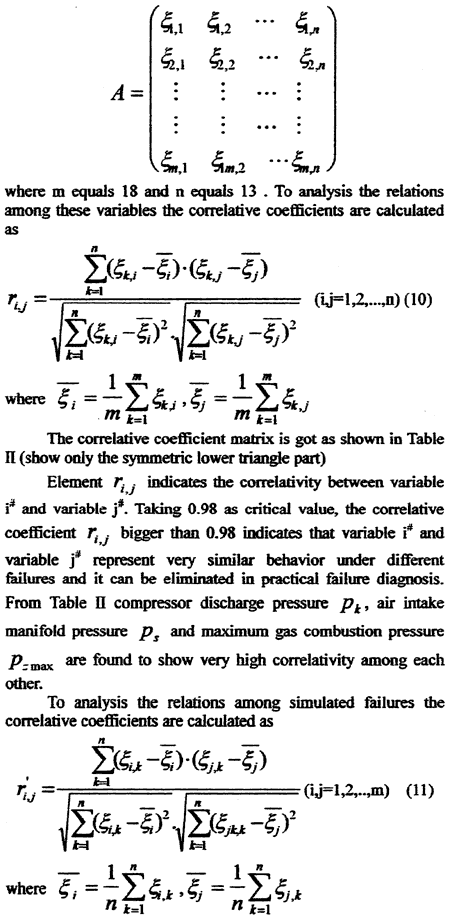
The correlative coefficient matrix is got as shown in Table III (shown only the symmetric lower triangle part).
Element r'i,j indicates the correlativity between failure i# and failure j#. Taking 0.95 as critical value, the correlative coefficients r' i,j bigger than 0.95 means failure i# and failure j# have very similar symptoms and is very difficult to be identified with these thermodynamic variables. It is found from Table III that there are 4 confusions in the identification of the 18 failures considered between blocked turbocharger exhaust casing (a) and worn turbocharger bearing (m) poorly cooled cylinder liner (e) and poorly cooled piston cap (f), retarded injection timing (o) and worn fuel pump plunger (p), 25 rudder angle adjusted (g) and 4 class wind encountered (r). To detect these failures more information have to be taken into account such as fuel injection pressure, inlet and outlet cooling water temperature, vibration or noise, etc.