Fracture stress (σ g) was decreased as test temperature decreased. It was confirmed that fracture stress of test specimen No. 13〜18 were more than standard yield point of used steel even at -90℃. And fracture stress of each test specimens No. F1〜F6 have tendency to be lower than No.13〜18. The reason is considered to be depending upon different condition of maternal, shape of test specimens and welding procedure. However, judging from the result at temperature, -10℃, which is lower 10℃ than design temperature of pressurized LPG tank normally, all test specimens were fractured over standard yield point of used steel. And condition of fracture was confirmed to be brittle fracture by high stress after ductile crack propagated but not unstable fracture by low stress. Then comparing of PWHT carried out and not at temperature -10℃ and -30℃, fracture stress was not so different each other.
(2) Critical stress intensity factor (Kc)
Relation between critical stress intensity factor and temperature on steel thickness 50mm is shown in Fig. 8. Relation between critical stress intensity factor and thickness at test temperature -10℃ is shown in Fig. 8. It was confirmed that critical stress intensity factor was decreased as test temperature decreased and steel thickness increased. And it was not so different between the result with PWHT carried out and not.
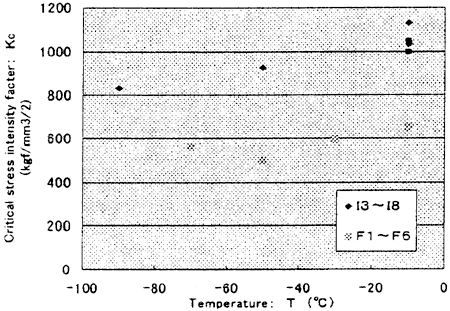
Fig. 9 Relation between critical stress intensity factor and temperature (thickness: 50mm)
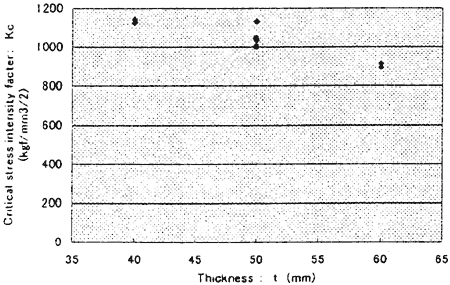
Fig. 8 Relation between critical stress intensity factor and thickness (Test temperature: -10℃ Test piece No. 11〜16, K1, K2)
(3) Critical COD (δc)
Whether brittle fracture occurs in welded construction or not is considered to be dominated by fracture toughness, existence of defects and condition of stress at welded parts. In case of actual pressurized LPG tank, most sensitive condition is considered to be having a surface crack on fusion line of T joint, where a longitudinal joint is crossed with a circumferential Joint.
In following evaluation, required COD would be decided in accordance with WES 2850[5], in which the method of estimation for defects in welding joints with respect to brittle fracture is required by The Japan Welding Engineering Society, comparing with critical COD calculated from actual test results.
1) Condition of assessment
Required COD for actual design condition is calculated for welding joint of LPG tank steel plate having thickness 40mm, 50mm and 60mm by assuming defects and considering manufacturing error and condition of allowable stress as follows
1] position of defect: T joint of LPG tank
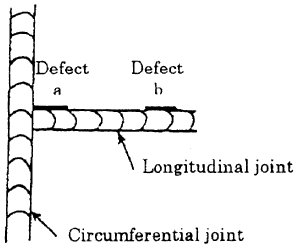
2] Assumed defect: Surface crack, Length: 30mm x Depth: 5mm
Above mentioned is assumed from consideration of the result of investigation for crack propagation due to fatigue which was reported by Spherical Gas Holder Research Committee as the result from research of tank opening inspection at Kanagawa-pref., size of any defects had found almost lower than the above. [6]
3] Manufacturing error:
・Defect a:
Amount of angular distortion : 0mm/1000mm
Alignment of butt weld: 3mm
・Defect b:
Amount of angular distortion: 13mm/1000mm
Alignment of butt weld: 3mm
4] Residual stress after welded
Defect a: 0.6 σy = 372 (N/mm2)
Defect b: 0.2 σy = 124 (N/mm2)
σy: Yield Point of steel grade KD63-M-PV (620N/mm2)
The above are in accordance with WES2805
5] Loaded stress:
・Hoop stress (σt): 240N/mm2, which is the design allowable stress. (T.S./3)
T.S.: Tensile stress of steel grade KD63-M-PV (720N/mm2:)
BACK CONTENTS NEXT