Both examples in Fig. 5 show a interesting pulsing In composition with intrusions of SP-dominated throughflow every 5 years or so. There are insufficient observations to confirm or refute this pulsing, but the general trend in both maps to a greater fraction of SP water mass over the last decade is consistent with salinity observations shown in Fig. 1.
It is noteworthy that for the ECMWF wind stresses, moderate nonlinearity is not sufficient to change the composition from being almost wholly SP, and interestingly, a similar calculation using wind stresses derived from SSM/I data, Atlas et al. (1996), gives a contradictory result. In that case, the throughflow is wholly fed by the Mindanao Current even when yN = 2.25。? corresponding to linear dynamics.
The above calculations are for a simple single channel entrance to the Indonesian archipelago, i.e. it is assumed that there is no flow through the Halmahera Sea. By defining two further channel operators based on ψh, ψs, the values of the streamfunction on Halmahera and Sulawesi respectively, the fractional composition in each of the entrance channels to the archipelago can be determined with the following result
Makassar Strait: CNP = S0[H0(N)], CSP = min(S, H) - S0[H0(X)]
Maluku Sea: CNP = S1[H0(N)] - S, CSP = max(S, H) - S1[H0(X)]
Halmahera Sea: CNP = H1(Y) - H, CSP = 1 - H1(P),
where X = max(N, P), Y = min(N, P),
and Ha(b) = median(a, ψh, b), Sa(b) = median(a, ψs, b). (2)
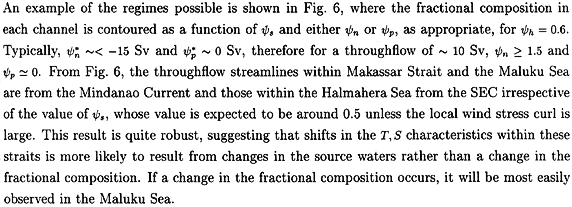
The result now depends on the value of the streamfunction at the interior edge of the Pacific western boundary layer at the northern tips of Halmahera, ψn, and Irian Jaya, ψp, or their nonlinear equivalents.