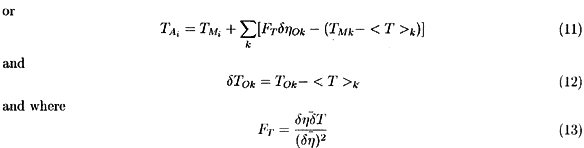Figure 3: Four flows at final time, day 70.
3.1 The Assimilation Method
The basic idea behind the new method is to use wavelet analysis to detect errors in the computational domain. Based on this fast real-time error analysis, we decide how to weight computed information against observed information. Simply stated, if the computational errors are large in a certain region of the computational domain at certain time, then the observed data will receive a relatively large weight. On the other hand, if the computational errors are small, then the computed information will be considered relatively reliable in this region and will be assigned a small weight. This new technique might be considered to be related to optimal interpolation or in the category of so-called nudging techniques. In the following equations η is the sea, surface height, T is the sea surface temperature, M represents the model result, O represents the observed data, A denotes the assimilated result also known as the analysis data, and the matrix P is the weighting matrix which determines the relative importance of the model and observed data. F is known as the correlation factor, and δT is the deviation from average value of T.