Figure 1: Western Mediterranean basin: tomographic observational array of Thetis 2 experiment and the limits of the model domain.
3 Variational assimilation of silmulated tomography data
The goal of data assimilation is to find the best fit between a model trajectory and observations distributed over a time interval. The dynamical model propagates informations from the data over the time and space domain. In our experiments, the control variables is the initial conditions x0. The solution is obtained by minimizing the cost function J which contains the misfit between the observations and their equivalent in the model and a regularization term R.
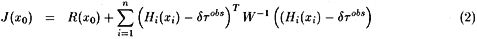
Since the minimum of J have to be found in the model domain of solutions, the model represents a strong constraint for the minimization problem. As the model is non-linear, the information can be transfered from the variables and scales directly contrained by the the data to others variables and scales. The minimization problem is solved by variational method, using the adjoint model to compute the sensitivity of the cost function J to the variations of initial conditions, x0. W is the covariance matrix of observational errors, here it is a diagonal matrix. To evaluate the ability of tomographic observations to constrain the model circulation, we assimilate observations simulated assimilation with the“true”state.