|
Fig.8
|
Appropriate handling by excellent teamwork in Navigation Bridge
|
Singapore Strait
|
Fig.9
|
Occurrence of overshooting caused by human insufficient behavior
|
Singapore Strait
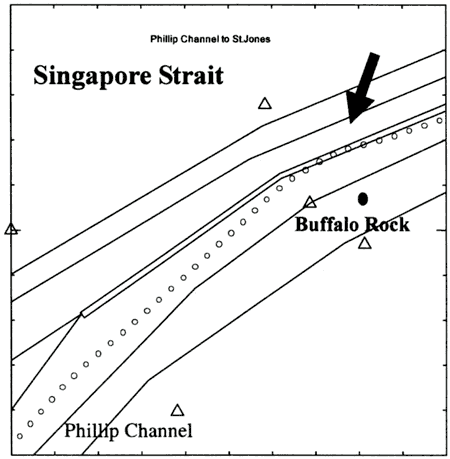
In figure 6 and figure 7, discs indicate the position of own vessel (bulk carrier) at every one-minute, and triangles indicate the position of the target vessel (VLCC). In figure 6, when a bulk carrier proceeded at the deep lane of Singapore Strait in west bound, Captain who is an Indonesian recognized crossing vessel that is the VLCC bound for Shell SBM (Sea Berth) from Phillip Channel. At that time, bulk carrier was sailing at the near central separate zone for overtaking the same course vessel. And Captain steered own vessel to starboard side slightly after recognition of the crossing vessel. At the point of 183 seconds before closest point, Captain tried to call the target vessel by himself using VHF Radio to confirm the intention of the VLCC, and Captain spent just 83 seconds to confirm the intention of the target vessel and to inform his intention to target vessel by VHF Radio. And Captain gave an order steer own course to starboard slightly to helmsman on just 16 seconds after finishing of communication by VHF Radio. As the result of analysis, it could be found that during 16 seconds. Captain confirmed current situation and estimated future situation using the change of compass bearing and the data of ARPA against the target vessel. However, in the same situation, it was already found that it was necessary to spend more than 16 seconds to confirm current situation and estimate future situation for maintaining safer ship's operation. At that time, proposal condition for an occurrence of human insufficient behavior was fulfilled. On the other hand, in figure 7, it was confirmed that there is no time to estimate the future situation. This is the same condition as figure 6. However, Captain gave an order, contact the target vessel using VHF Radio immediately, to 2/O at the point of 194 seconds before closest point. However, 2/O didn't execute that order immediately. Before a calling, 2/O tried to confirm the navigation data of target vessel using ARPA. As Captain was impatient of 2/O's behavior, he tried to call the target vessel by himself using VHF Radio at the point of 138 seconds before closest point. During a calling, 2/O took Captain's place that was the role of VHF Radio operation for communication with target vessel. And it could be found that 2/O spent 120 seconds to confirm the intention of the target vessel. During communication with the target vessel, Captain steered own course to starboard to avoid abnormal closing. And at the point of 18 seconds before closest point, Captain gave an order Port 20 to helmsman. However, bulk carrier was stuck out from the fairway as the result. At that time, it could be confirmed that there is no time to estimate future situation. This situation exactly corresponds to abnormal situation (3). Furthermore, the similar situation caused by human insufficient behavior could be confirmed in other illustrations. The fairways in figure 8 and figure 9 indicate a part of Singapore Strait, where is the palace between Phillip Channel and Buffalo Rock. And discs indicate the position of own vessel (VLCC) at every one-minute, and black disk indicates the position of the target vessel (container Vessel). Figure 8 indicates the appropriate handling by excellent teamwork in Navigation Bridge. When the VLCC proceeded at the deep lane of Singapore Strait in east bound, she avoided the container vessel that adrift in vicinity Buffalo Rock for taking a pilot. The container vessel, being at a standstill, intends to entry to the port of Singapore from eastbound shallow lane after taking a harbor pilot. In this situation, VLCC is own vessel and target vessel is the container vessel. Captain of the VLCC gave an order contact the container vessel using VHF Radio immediately to 2/O at the point of 247 seconds before passing Buffalo Rock. 2/O obeyed the Captain's order immediately and told his Captain's intention; intend to pass on the head of container vessel, to the target vessel. At that time, 2/O spent just 72 seconds to inform his Captain's intention to her by VHF Radio. Consequently, attainable time to alter own course before passing Buffalo Rock was 175 seconds, and Captain did it safely with sufficient spare time. On that occasion, the relation between required a competency and attainable competency on the second task was shown as Q < C. Meanwhile, another Captain in the bridge team on figure 9 was just promoted to the mariner master at that time. At the same situation in Singapore Strait, the Captain gave orders that contact the container vessel using VHF Radio immediately and asks intention of the target vessel at the point of 105 seconds before passing Buffalo Rock. 2/O obeyed his Captain's orders and asked intention of container vessel by VHF Radio. However, 2/O could not communicate them within appropriate time. And as Captain was impatient of 2/O's behavior, he took part in that communication indirectly throughout the whole of it. As the result, Captain and 2/O spent just 145 seconds for communication to the target vessel by VHF Radio. As the result, the Captain lost the chance to give an order to alter her course, and the VLCC made an invasion upon the central separate zone shown in figure 9 against Captain's wishes. On that occasion, the relation between required competency and attainable competency was shown as C = NIL. These situations exactly correspond to abnormal situation (3) in figure 4. As mentioned above, it is clarified that risky situation caused by human insufficient behavior occur on ship's operations by not only single watch but also bridge team on duty. From results of the se analyses, it was confirmed that human insufficient behavior would occur when the required competency by navigational environment beyond the attainable competency by mariner. And, it was also found that human insufficient behavior tended to occur on the complex techniques.
Fig. 10 |
The one of characteristics of human insufficient behavior |
Fig. 11 Summary of experiment
Fig. 12 Result of experiments
5.2 Characteristics of Human Insufficient Behavior
In previous section, it was confirmed that human insufficient behavior is apt to occur when the balance between required competency by navigational environment and attainable competency by mariner was broken. In this section, the characteristic of human insufficient behavior was discussed. It has been confirmed that human insufficient behavior occurred with high frequency under restricted conditions. However, all of human insufficient behavior would not cause for marine accidents. Therefore the risk of marine accidents caused by human insufficient behavior was investigated. Generally speaking, it is thought that DCPA (Distance to Closest Point of Approach) is one of the standards for decision of risky situation. Then, DCPA between own vessel and the vessel corresponding to abnormal closing caused by human insufficient behavior was defined as the parameter of risk for an accident. And the correlation between the risk of marine accidents and a difference between required competency by navigational environment and attainable competency by mariner was researched. The research was executed about abnormal closing caused by human insufficient behavior concerning "Communication by VHF radio" and "Maneuvering for collision avoidance" in the same navigational environment. The number of sample is 20 cases. Figure 10 shows the relation of them. In figure 10, vertical axis indicates DCPA (mile) and horizontal axis indicates the difference between the attainable competency by an operator who has 1 st grade license and the required competency by navigational environment. And negative part in figure 10 indicates the situation in which human insufficient behavior occurred. Moreover, "r" in figure 10 shows the correlation coefficient. As the result of this research, the correlation coefficient of 0.83 between the risk of marine accidents and the difference between required and attainable competency was obtained, and it was confirmed that the risk of marine accidents would be raised as a difference between required and attainable competency increases. Furthermore. experimental verification was carried out using ship-handling simulator in Tokyo University of Mercantile Marine. Figure 11 shows summary of the experiment. Experiments were executed on 10 university students who had had 3 months on-board experience as a cadet. 2 kinds of tasks "Positioning" and "Planning", were given to the subjects. Each quantity of required competency can be obtained from Figure 1 (a) and (b). And after accomplishment of these tasks, the subjects have to alter own course in accordance with the plan made by themselves. However, if a subject gives an order to alter course at the point after line of limit, overshooting will be happen. On the other hand, all subjects were familiar with the maneuverability of subjective vessel and how to determine the altering, point, as they underwent the training and lecture for familiarization before experiments. Then, for making the condition for an occurrence of human insufficient behavior, the initial position was set up at the point of 300 seconds before altering point. Consequently, the condition, Q2 > C2, was fulfilled in this situation. Figure 12 indicates the result of the experiments. In figure 12, vertical axis indicates the difference between the required competency by given tasks and the attainable competency by subjects, and horizontal axis indicates the deviation value of overshooting. Moreover, "r" in figure 12 shows the correlation coefficient. As the result of this experiment, the correlation coefficient of 0.85 between the deviation value of overshooting and the difference between required competency and attainable competency could be obtained. Consequently, the characteristics of human insufficient behavior could be verified. The risk upon the safety degree on ship's operations would be raised as a difference between required and attainable competency increases.
6. CONCLUSION
The principal results of this study are shown as follows;
(1) It was clarified that human insufficient behavior would occur when a quantity of required competency by navigational environment beyond a quantity of attainable competency by mariner.
(2) It was confirmed that the risk of marine accidents would be raised as a difference between required competency by navigational environment and attainable competency by mariner increases.
(3) It was confirmed that human insufficient behavior on ship's operations occurred in the navigation watch by not only single officer but also plural officers such as a bridge team.
(4) The formulation, which is the condition for an occurrence of human insufficient behavior, was proposed.
REFERENCES
[1] Hiroaki KOBAYASHI. "Necessary Technique for Bridge Team Management", Proc. of INSLC 12, California Maritime Academy, Vallejo, California, USA, 2002
[2] Shin MURATA and Hiroaki KOBAYASHI, "Study on the Condition of an Occurrence of Human Error on Ship's Operations", Proc. of MARTECH'02, Singapore Maritime Academy, Singapore, 2002
[3] Shin MURATA and Hiroaki KOBAYASHI, "Study on the Condition of an Occurrence of Human Error on Ship's Operations (2)", Proc. of Workshop, 3rd Korea-Japan Workshop on Marine Simulation, Korea Maritime University, Busan Korea, 2003
[4] Hiroaki KOBAYASHI, et al, "Developing of Ship-handling Techniques into the Elemental Techniques and proposal of Education/Training Methods Utilizing Ship-handling Simulator", Proc. of IMLA, St. John's, Canada, 1997
[5] Hiroaki KOBAYASHI, et, al, "New Standards of MET using Ship-handling Simulator", Proc. of MARSIM2000, Orland Florida, USA, pp. 159-171, 2000
AUTHOR'S BIOGRAPHY
Shin MURATA is an associate professor of National Institute for Sea Training, JAPAN. He has had 11 years' on-board experience as a navigation officer on Japanese training ships. And he is a graduate student of doctoral course at Tokyo University of Mercantile Marine. His major fields are Education and Training, Human Factor and Human-machine system analysis on ship's operation. At this moment in time, he is belonging to the practical training bureau / research division of NIST, JAPAN.
|