|
6.2.4.2 Test samples
Each test sample consists of two pieces of the material from which the TPA is constructed, each of which is 100 mm square. The two pieces shall joined by a seam as shown in figure 1. For each type of seam, 5 samples shall be tested. Each sample may be cut from a TPA or may be prepared specifically for this test.
NOTE |
One type of seam is distinguished from another by the type and size of stitch or other joining method used (including orientation of warp and fill, if any) and by the type and thickness of the materials joined at the seam. |
| (拡大画面:134KB) |
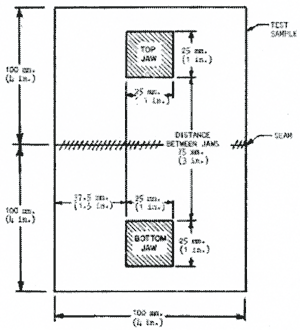 |
Figure 1 - |
Configuration for testing of seam strength |
6.2.4.3 Test procedure
Each sample shall be conditioned for at least 40 hours at 25.℃ ± 2℃ and 50% ± 5% relative humidity. Immediately after conditioning, each sample shall be mounted individually in the tension device as shown in figure 1 . The jaws shall be separated at a rate of 5 mm/second. The maximum force to achieve rupture shall be recorded. The average force at rupture shall be at least 225 N.
[Alternatively, refer to ISO 13934-2:1999 Textiles - Tensile properties of fabrics - Part 2: Determination of maximum force using the grab method? Does it adequately cover procedure?]
6.2.5 Tear resistance
The tear resistance of the material from which a TPA is constructed shall be determined by the method described in [ASTM D 1004][ISO 4674:1977][ISO 6383-1 :1983][ISO 9073-4:1997]. If more than one material is used, each material shall be tested. If varying thicknesses of a material are used in the TPA, samples representing the thinnest portion of the material shall be tested. If multiple layers of a material are used in the TPA, samples representing the exterior layer shall be tested. Any composite formed of two or more fabrics or films bonded together is considered to be a single fabric or film. The average tearing strength of each material shall be at least [45N].
6.2.6 Temperature cycling test
6.2.6.1 Two samples of the TPA, in their original packaging, shall be alternately subjected to surrounding temperatures of -30.℃ to +65℃. These alternating cycles need not follow immediately after each other, and the following procedure, repeated for a total of ten cycles, is acceptable:
a) 8 h conditioning at 65.℃±2℃ to be completed in one day
b) |
The specimens removed from the warm chamber that same day and left exposed under ordinary room conditions until the next day; |
c) 8 h conditioning at - 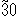 .℃±2℃ to be completed the next day
d) |
The specimens removed from the cold chamber that same day and left exposed under ordinary room conditions until the next day. |
6.2.6.2 The TPA's shall not show any damage, such as shrinking, cracking, swelling, dissolution or change of mechanical qualities.
7 Marking
7.1 Each TPA shall be marked with:
a) |
the words "Thermal Protective Aid" in the appropriate language or languages, and/or the appropriate IMO symbol from IMO Res. A.760(18); |
b) the name of the manufacturer;
c) the model;
d) |
the date of manufacture, or a lot number from which the date of manufacture may be determined; |
e) relevant approval information.
7.2 The packaging of the TPA shall be marked with the words in accordance with 7.1 (a), or the similar markings on the TPA shall be visible through the packaging.
8 Production testing
8.1 One out of every 100 TPA's produced shall be given a complete visual examination against the approved plans. Samples shall be selected at random from a production lot of 100 TPA's. The sample fails if the visual examination shows that the TPA does not conform to the approved design.
8.2 If a defect in the TPA is detected upon visual examination, 10 additional samples from the same lot shall be selected at random and examined for the defect.
8.3 If one or more of the 10 samples fails the examination, each TPA in the lot shall be examined for the defect for which the lot was rejected. Only thermal protective aids that are free of defects may be considered to comply with this International Standard.
|